Bookish Thoughts: What is AI?
We're going to start with some terms. This is just one part of what I have to say.
A Pre-Ramble
It is only March, but AI is already looking like one of or the topic of the book world in 2024. That is whether we like it or not. If we need to face debates and deep discussions about something big then we have to get our vocabulary straight.
So if we are all going to be pulled into to the news of…
we might as well try to get straight about what is being talked about.
This is part one of an evolving commentary I am creating and planning to talk about with my fellow hostesses on Tales from the Orc Den. The focus on this installment is basic vocabulary breakdowns based on my personal observations of Internet discourse and a little more.
Part 1: What is AI? (That’s this part)
Part 2: Who are AI's Major Players?
Part 3: Where can we go from here in this AI world?
Below I have some basic vocabulary breaking down what AI is in its basic sense from the computer science discipline. I also want to break down some basic kinds of AI and major software playing a part in these major discussions. The emphasis is basic here and the focus is on being a reference.
Breaking Out Common AI Terms
Computer Science
The study of computational systems and computers (like whatever you are using to read this).
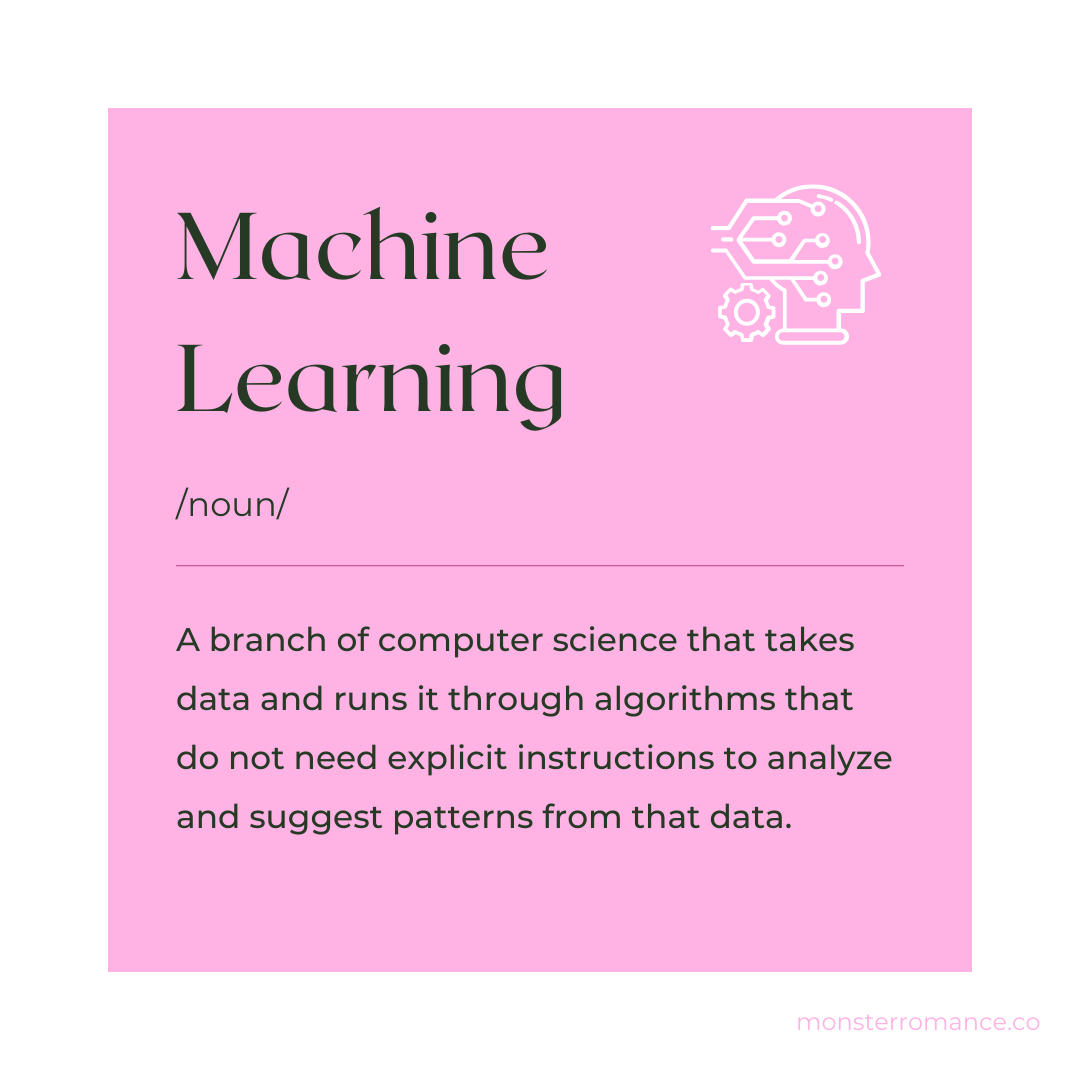
Machine Learning
A branch of computer science that takes data and runs it through algorithms that do not need explicit instructions to analyze and suggest patterns from that data.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
A branch of Machine Learning focused on taking training data and building on it with computational variations to tackle complex operations that have typically required humans.
Training Data
A required component of AI algorithms and other machine learning algorithms. AI results seek patterns guided by prompts, using its training data, and having “learned” from it.
Algorithm
A sequence of commands written in computer-readable code to perform calculations or a required process.
Generative Artificial Intelligence
Requires minimal human activity, typically encapsulated in a singular text prompt, to deliver a final product.
Examples: Art generator, text generator, video generator
Assistive Artificial Intelligence
Requires frequent, involved human activity to deliver a final product.
Examples: audio-to-transcript generators, photo editing automation, screen readers, grammar assistants, medical assistants
Housekeeping
For more information about this newsletter’s spice and star system, check out this newsletter’s About Me page.